Network setup¶
This guide shows how to create a DHCP/TFTP/DNS network boot environment to boot and provision BIOS/PXE, iPXE, or UEFI client machines.
Matchbox serves iPXE scripts over HTTP to serve as the entrypoint for provisioning clusters. It does not implement or exec a DHCP, TFTP, or DNS server. Instead, configure your network environment to point to Matchbox or use the convenient quay.io/poseidon/dnsmasq container image (used in local QEMU/KVM setup).
Note: These are just suggestions. Your network administrator or system administrator should choose the right network setup for your company.
Requirements¶
Client hardware must have a network interface which supports PXE or iPXE.
Goals¶
- Add a DNS name which resolves to a
matchboxdeploy. - Chainload BIOS clients (legacy PXE) to iPXE (undionly.kpxe)
- Chainload UEFI clients to iPXE (ipxe.efi)
- Point iPXE clients to
http://matchbox.example.com:port/boot.ipxe - Point GRUB clients to
http://matchbox.example.com:port/grub
Setup¶
Many companies already have DHCP/TFTP configured to "PXE-boot" PXE/iPXE clients. In this case, machines (or a subset of machines) can be made to chainload from chain http://matchbox.example.com:port/boot.ipxe. Older PXE clients can be made to chainload into iPXE to be able to fetch subsequent configs via HTTP.
On simpler networks, such as what a developer might have at home, a relatively inflexible DHCP server may be in place, with no TFTP server. In this case, a proxy DHCP server can be run alongside a non-PXE capable DHCP server.
This diagram can point you to the right section(s) of this document.
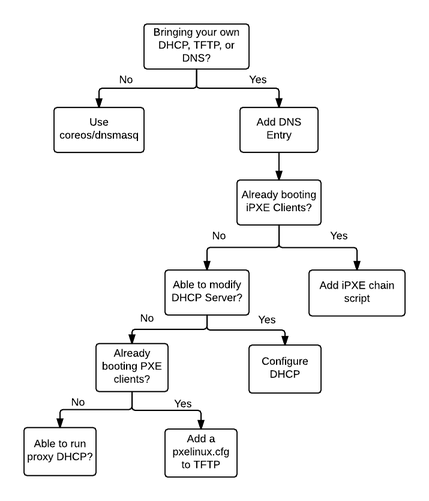
The setup of DHCP, TFTP, and DNS services on a network varies greatly. If you wish to use Docker to quickly run DHCP, proxyDHCP TFTP, or DNS services, use poseidon/dnsmasq.
DNS¶
Add a DNS entry (e.g. matchbox.example.com, provisoner.mycompany-internal) that resolves to a deployment of the CoreOS matchbox service from machines you intend to boot and provision.
$ dig matchbox.example.com
If you deployed matchbox to a known IP address (e.g. dedicated host, load balanced endpoint, Kubernetes NodePort) and use dnsmasq, a domain name to IPv4/IPv6 address mapping could be added to the /etc/dnsmasq.conf.
# dnsmasq.conf
address=/matchbox.example.com/172.18.0.2
iPXE¶
Networks which already run DHCP and TFTP services to network boot PXE/iPXE clients can add an iPXE config to delegate or chain to the matchbox service's iPXE entrypoint.
# /var/www/html/ipxe/default.ipxe
chain http://matchbox.example.com:8080/boot.ipxe
You can chainload from a menu entry or use other iPXE commands if you need to do more than simple delegation.
PXE-enabled DHCP¶
Configure your DHCP server to supply options to older PXE client firmware to specify the location of an iPXE or GRUB network boot program on your TFTP server. Send clients to the matchbox iPXE script or GRUB config endpoints.
Here is an example /etc/dnsmasq.conf:
dhcp-range=192.168.1.1,192.168.1.254,30m
enable-tftp
tftp-root=/var/lib/tftpboot
# Legacy PXE
dhcp-match=set:bios,option:client-arch,0
dhcp-boot=tag:bios,undionly.kpxe
# UEFI
dhcp-match=set:efi32,option:client-arch,6
dhcp-boot=tag:efi32,ipxe.efi
dhcp-match=set:efibc,option:client-arch,7
dhcp-boot=tag:efibc,ipxe.efi
dhcp-match=set:efi64,option:client-arch,9
dhcp-boot=tag:efi64,ipxe.efi
# iPXE - chainload to matchbox ipxe boot script
dhcp-userclass=set:ipxe,iPXE
dhcp-boot=tag:ipxe,http://matchbox.example.com:8080/boot.ipxe
# verbose
log-queries
log-dhcp
# static DNS assignments
address=/matchbox.example.com/192.168.1.100
# (optional) disable DNS and specify alternate
# port=0
# dhcp-option=6,192.168.1.100
Add ipxe.efi and unidonly.kpxe to your tftp-root (e.g. /var/lib/tftpboot).
$ sudo systemctl start dnsmasq
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=dhcp --add-service=tftp [--add-service=dns]
$ sudo firewall-cmd --list-services
See dnsmasq below to run dnsmasq with a container.
Proxy-DHCP¶
Alternately, a proxy-DHCP server can be run alongside an existing non-PXE DHCP server. The proxy DHCP server provides only the next server and boot filename Options, leaving IP allocation to the DHCP server. Clients listen for both DHCP offers and merge the responses as though they had come from one PXE-enabled DHCP server.
Example /etc/dnsmasq.conf:
dhcp-range=192.168.1.1,proxy,255.255.255.0
enable-tftp
tftp-root=/var/lib/tftpboot
# if request comes from older PXE ROM, chainload to iPXE (via TFTP)
pxe-service=tag:#ipxe,x86PC,"PXE chainload to iPXE",undionly.kpxe
# if request comes from iPXE user class, set tag "ipxe"
dhcp-userclass=set:ipxe,iPXE
# point ipxe tagged requests to the matchbox iPXE boot script (via HTTP)
pxe-service=tag:ipxe,x86PC,"iPXE",http://matchbox.example.com:8080/boot.ipxe
# verbose
log-queries
log-dhcp
Add unidonly.kpxe (and undionly.kpxe.0 if using dnsmasq) to your tftp-root (e.g. /var/lib/tftpboot).
$ sudo systemctl start dnsmasq
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=dhcp --add-service=tftp [--add-service=dns]
$ sudo firewall-cmd --list-services
See dnsmasq below to run dnsmasq with a container.
Configurable TFTP¶
If your DHCP server is configured to network boot PXE clients (but not iPXE clients), add a pxelinux.cfg to serve an iPXE kernel image and append commands.
Example /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default:
timeout 10
default iPXE
LABEL iPXE
KERNEL ipxe.lkrn
APPEND dhcp && chain http://matchbox.example.com:8080/boot.ipxe
Add ipxe.lkrn to /var/lib/tftpboot (see iPXE docs).
poseidon/dnsmasq¶
The quay.io/poseidon/dnsmasq container image can run DHCP, TFTP, and DNS services via docker. The image bundles ipxe.efi, undionly.kpxe, and grub.efi for convenience. See contrib/dnsmasq for details.
Run DHCP, TFTP, and DNS on the host's network:
sudo docker run --rm --cap-add=NET_ADMIN --net=host quay.io/poseidon/dnsmasq \
-d -q \
--dhcp-range=192.168.1.3,192.168.1.254 \
--enable-tftp --tftp-root=/var/lib/tftpboot \
--dhcp-match=set:bios,option:client-arch,0 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:bios,undionly.kpxe \
--dhcp-match=set:efi32,option:client-arch,6 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:efi32,ipxe.efi \
--dhcp-match=set:efibc,option:client-arch,7 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:efibc,ipxe.efi \
--dhcp-match=set:efi64,option:client-arch,9 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:efi64,ipxe.efi \
--dhcp-userclass=set:ipxe,iPXE \
--dhcp-boot=tag:ipxe,http://matchbox.example.com:8080/boot.ipxe \
--address=/matchbox.example.com/192.168.1.2 \
--log-queries \
--log-dhcp
Run a proxy-DHCP and TFTP service on the host's network:
sudo docker run --rm --cap-add=NET_ADMIN --net=host quay.io/poseidon/dnsmasq \
-d -q \
--dhcp-range=192.168.1.1,proxy,255.255.255.0 \
--enable-tftp --tftp-root=/var/lib/tftpboot \
--dhcp-userclass=set:ipxe,iPXE \
--pxe-service=tag:#ipxe,x86PC,"PXE chainload to iPXE",undionly.kpxe \
--pxe-service=tag:ipxe,x86PC,"iPXE",http://matchbox.example.com:8080/boot.ipxe \
--pxe-service=tag:#ipxe,X86-64_EFI,"PXE chainload to iPXE UEFI",ipxe.efi \
--pxe-service=tag:ipxe,X86-64_EFI,"iPXE UEFI",http:///matchbox.example.com:8080/boot.ipxe \
--log-queries \
--log-dhcp
Be sure to allow enabled services in your firewall configuration.
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=dhcp --add-service=tftp --add-service=dns
UEFI¶
Development¶
Install the dependencies for QEMU with UEFI. Walk through the getting-started-with-docker tutorial. Launch client VMs using create-uefi.
Create UEFI QEMU/KVM VMs attached to the docker0 bridge.
$ sudo ./scripts/libvirt create-uefi
UEFI clients should chainload ipxe.efi, load iPXE and Ignition configs from Matchbox, and Container Linux should boot as usual.
Troubleshooting¶
See troubleshooting.